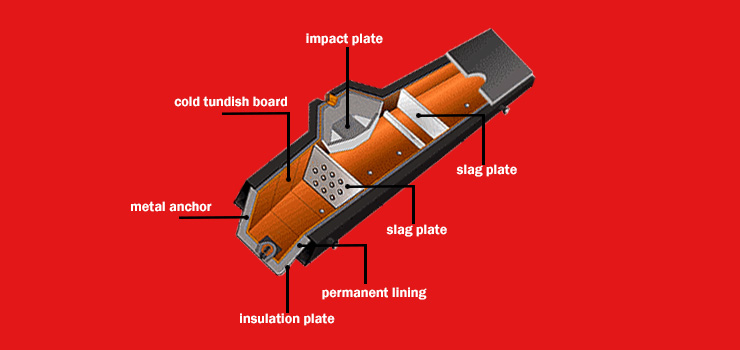
Ladle is a device used to wrap and protect molten steel during the steelmaking process. It requires the use of refractory materials that are resistant to factors such as high temperature, thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Here are some refractory materials that can be used for intermediate pots:
Magnesia Carbon Bricks (MgO-C Bricks): This type of brick is made of magnesium oxide and graphite. It has high heat resistance and thermal shock resistance, and is suitable for high temperature melting environments.
High alumina bricks: High alumina bricks are mainly composed of high alumina minerals. They maintain stability at high temperatures and have good corrosion resistance. They are suitable for melting processes containing elements such as aluminum and silicon.
Carbon bricks: Carbon bricks are mainly made of carbon materials such as graphite. They have excellent thermal conductivity and heat resistance and are suitable for parts requiring high thermal conductivity.
Refractory material: Unlike refractory bricks, refractory material is a refractory material that can fill various shaped spaces in the middle pot and adapt to complex packaging requirements. Its composition can include high-aluminum aggregate, high-alumina cement, etc. to ensure resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion.
Refractory fiber: Refractory fiber is often used to fill the small gaps in the middle pot, providing additional thermal protection while providing better resistance to thermal shock.
Lining material: The lining material is the part of the ladle that is in direct contact with the steelmaking liquid and must have certain corrosion resistance. It can be made of refractory aggregate, high alumina cement, etc. to protect the middle basin from chemical attack.
Fire-resistant coating: This coating can be applied to the inner wall of the tundish to provide a protective film that prevents interaction between the steelmaking liquid and the tundish wall.
The selection of tundish refractory materials will be adjusted according to the specific smelting process, material composition and temperature requirements to ensure the stability and durability of the tundish in high-temperature smelting environments.