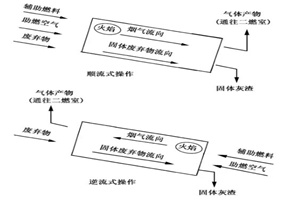
According to the different flow directions of gas and solid in the rotary kiln, the rotary kiln can be divided into two types: co-current flow kiln and counter-current flow kiln.
In the downstream operation mode, the preheating, combustion and burnout stages of hazardous waste are more obvious in the kiln. The layout of the feed, air intake and auxiliary burners is simple, and the operation and maintenance are convenient, which is conducive to the feeding and pre-processing of the waste. treatment, while the flue gas residence time is longer.
In the countercurrent operation mode, the rotary kiln can provide better gas-solid mixing and contact, high heat transfer efficiency, and can increase its combustion speed. However, the countercurrent operation method requires a complex feeding system and a slag removal system, which is costly. At the same time, due to the high relative velocity of gas and solid, the amount of dust carried away by the flue gas is relatively high, which increases the control of the combustion conditions and flue gas in the rotary kiln. Difficulty of dwell time.
Therefore, the downstream rotary kiln incinerator is more suitable for the treatment of hazardous waste and is more widely used.
Rotary kiln can be divided into slag rotary kiln (Slagging rotary kiln) and non-slagging rotary kiln (Non-slagging rotary kiln) according to the different ash state and furnace temperature during combustion in the rotary kiln. Among them, the non-slag type is also called “ash type”.
The temperature of the slag type rotary kiln is much higher than that of the non-slag type rotary kiln, which may bring the following problems: the rotary kiln requires higher refractory materials and insulation materials; the material cost of the feeding system and the combustion-supporting system increases and the operating life is increased. Short time; large consumption of auxiliary materials during operation, more expensive; high content of heavy metals and NOx in flue gas, which increases the cost of subsequent flue gas treatment. Although the slag type rotary kiln has a low slag reduction rate and complete incineration, it is not dominant considering the operating cost and the service life of the refractory material. Therefore, the non-slag rotary kiln is more economical and practical than the slag type in the field of hazardous waste treatment, and is more and more widely used in engineering.